
Ginsenosides
“What is Ginsenosides?”
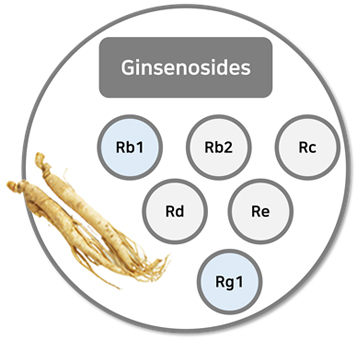 |
Ginseng is an important herb that has maintained the health of our people for over 2,000 years, as it is recorded in the oldest herbal medicine book, ‘Shin-non-bon-cho-gyeong’, to nourish the five organs and stabilize the mind. Ginsenosides means a glycoside specifically present in Ginseng |
 Ginsenosides exist in the roots, stems, leaves, barks, and seeds of plants. It has a different chemical structure from saponin found in other plants, and has unique physiological effects. In the past, it was known as a non-nutritional substance, but recently it has been attracting attention as a physiologically active substance as anti-cancer, antioxidant, and immune enhancing effects have been revealed. Ginsenosides are largely divided into two types according to the basic form in which no sugar is attached. One is the tetracyclic dammarane system, and the other is the pentacyclic oleanane system. If the number of hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the dammarene system is two, it is classified as Protopanaxadiol (PPD), and if it is three, it is classified as protopanaxatriol (PPT). The names are different depending on the sugar attached to the hydroxyl group, and about 32 types of ginsenosides have been identified in Korean ginseng to date. 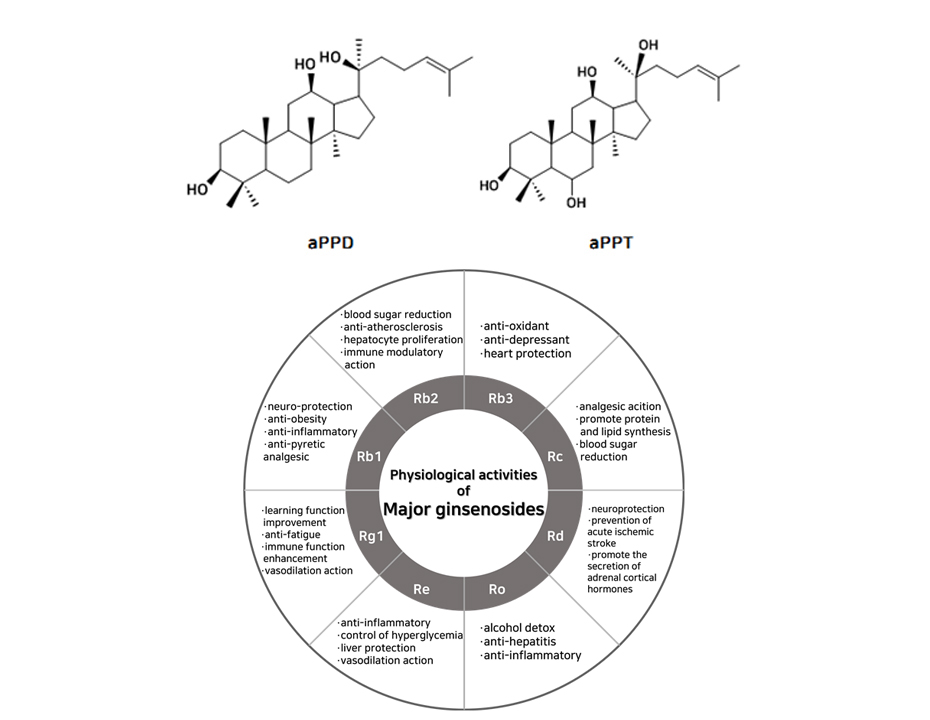
|
|
“What is Rare ginsenosides?”
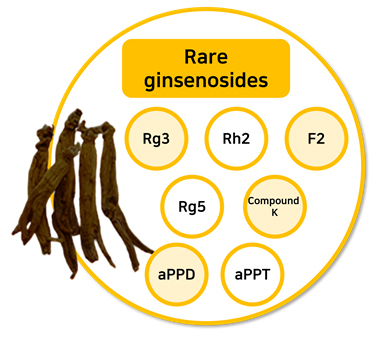 |
he main ginsenosides that ginseng originally has are Rb1, Rg1, and Rb2, which account for more than 80% of the total content. These ginsenosides have a large molecular weight, so the absorption rate in the body is low. There is also a research result that 37.5% of Korean can't absorb ginsenosides due to lack of microorganisms that can decompose it. (Ref.: Ham et. al,. JKSFSN, 2004. 11, 17~19) |
| However, when ginseng is processed such as steaming and drying, the sugars of major ginsenosides are decomposed and changed to a form with a lower molecular weight. This is a rare ginsenoisdes, such as Rg3 and compound K. Rare ginsenosides are small in molecular weight and highly absorbable in the body, and are present only in trace amounts in red and black ginseng. Rare ginsenosides have different physiological activities than major ginsenosides. 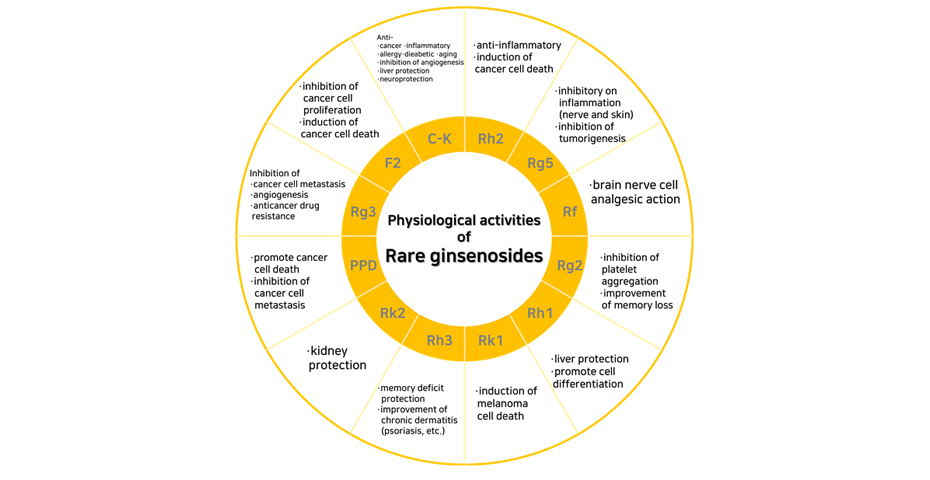 |
|
